In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have identified 2700 enhancers crucial for regulating genes responsible for bone growth. This discovery sheds new light on how these non-coding genetic sequences influence the size and development of individuals, potentially explaining certain bone malformations.
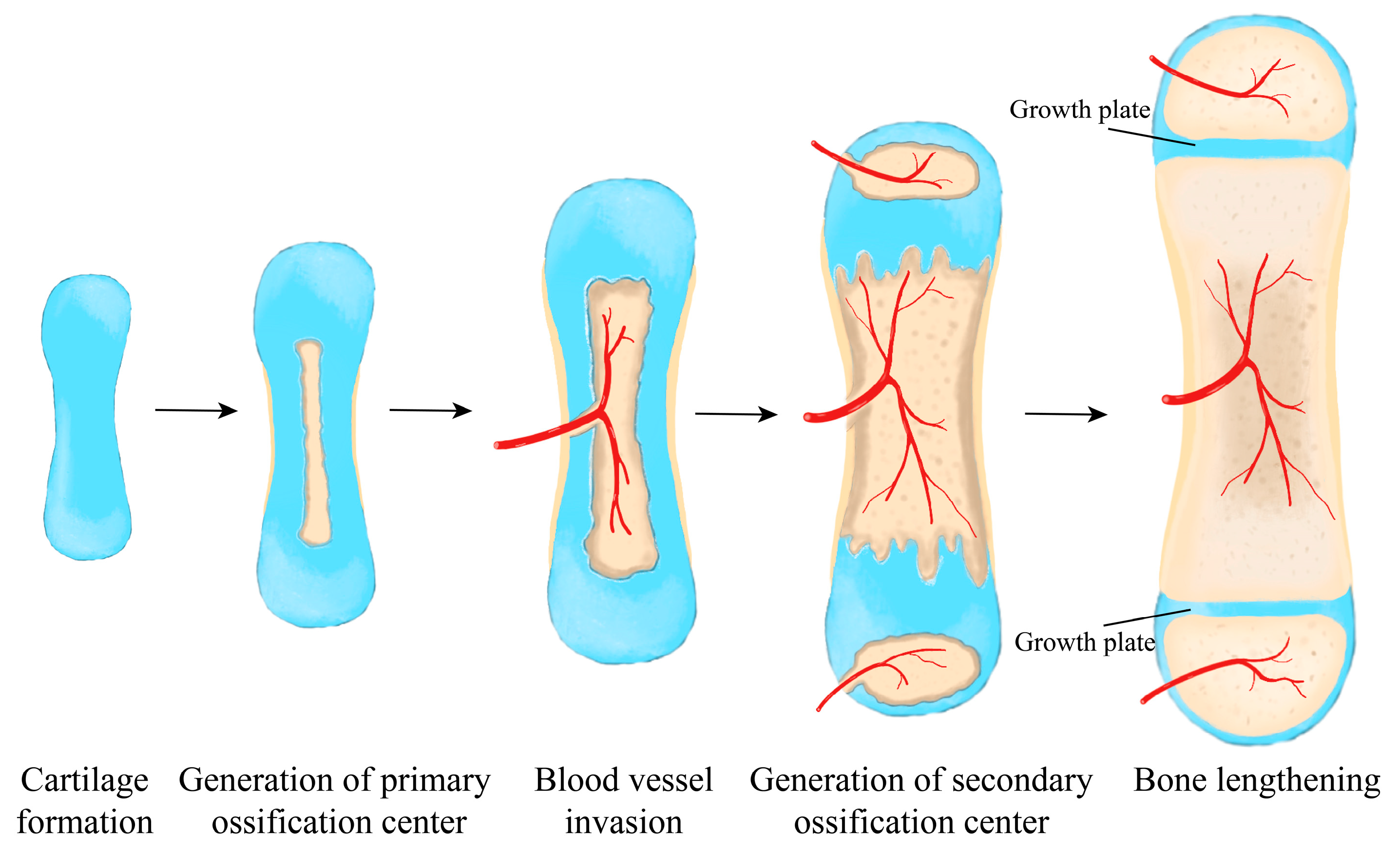
Understanding Enhancers in Genetic Regulation
Enhancers are like switches in the genome that activate or deactivate genes, playing a pivotal role in controlling biological functions such as bone formation. Despite extensive knowledge about genes involved in bone growth, understanding the regulatory mechanisms behind them has been limited until now.
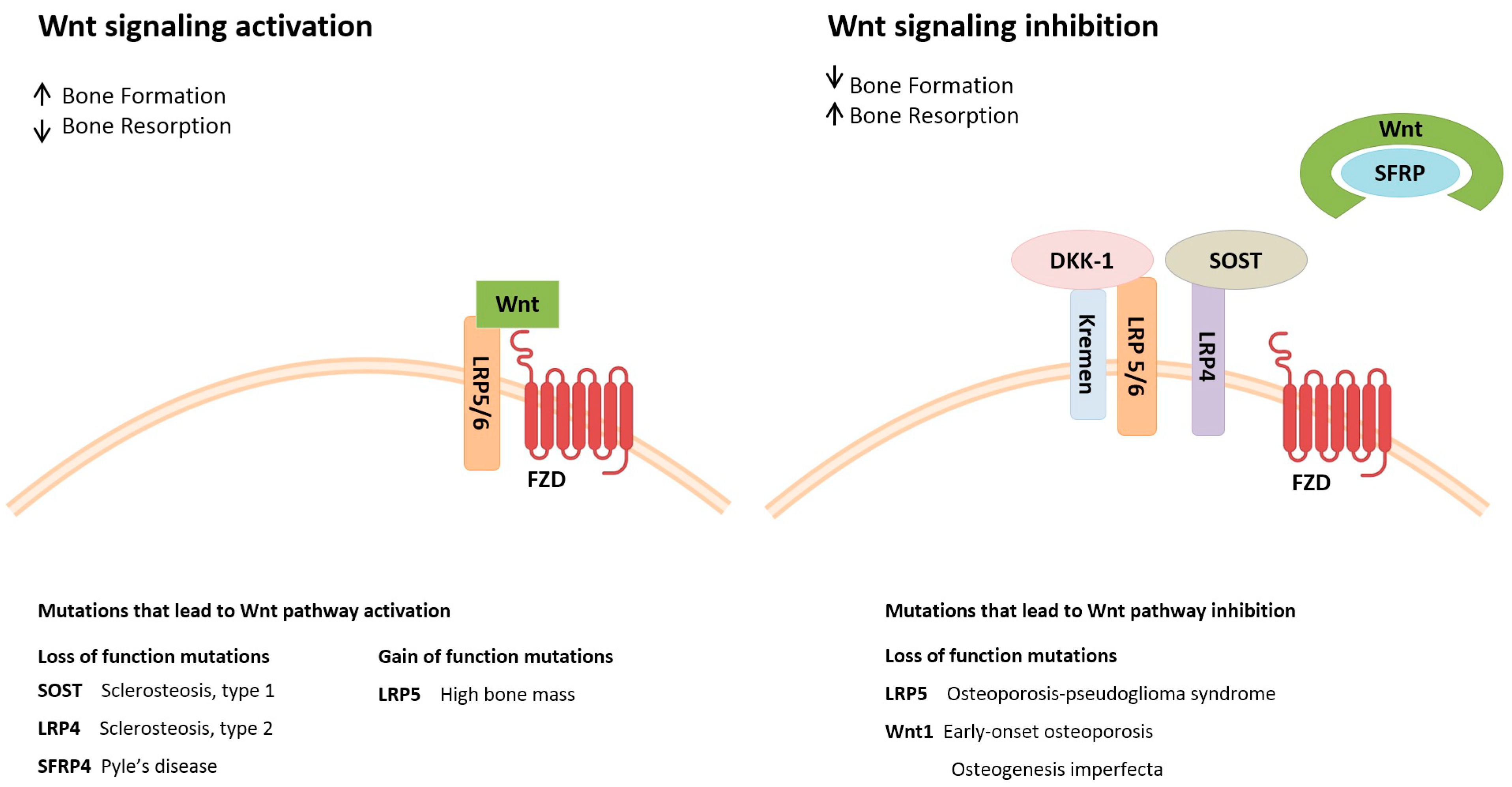
Experimental Breakthrough
Led by Guillaume Andrey at UNIGE, the research team developed an innovative technique using fluorescent bone cells in mouse embryos. This method allowed them to pinpoint which enhancers activate genes during bone development, providing crucial insights into their regulatory roles.
Biotechnological Implications
Maxanim, a leading supplier in biotech products, plays a crucial role in advancing research capabilities through innovative solutions. Their expertise in providing specialized tools and technologies supports groundbreaking studies like those at UNIGE, facilitating discoveries in genetic medicine and developmental biology.
Potential Applications in Healthcare
Understanding how enhancers influence bone growth could revolutionize healthcare, offering new avenues for diagnosing and treating genetic diseases affecting skeletal development. By focusing on regulatory regions rather than coding genes, researchers may uncover novel therapeutic targets.
Future Prospects
As research continues to uncover the complexities of genetic regulation, advancements in biotechnology will be pivotal. Companies like Maxanim remain integral in providing state-of-the-art tools that empower researchers to explore new frontiers in genetic medicine and precision healthcare.
Conclusion
The identification of enhancers regulating bone growth marks a significant leap in understanding genetic influences on human health. This research not only enhances our knowledge of skeletal development but also opens doors to potential treatments for a wide range of genetic disorders. As science progresses, collaborations between academia and industry, supported by companies like Maxanim, promise continued breakthroughs in biotechnology and genetic medicine.